Free Funnel Audit
Convert more customers today!

SEO
10 mins read


SEO
10 mins read


Moving applications to the cloud can feel confusing for many teams today because the process includes many steps. Clear cloud migration strategies help companies plan better and avoid unexpected issues during the move.
These strategies offer simple guidance that supports every decision and helps teams work with confidence.
Many companies first learned these methods from AWS, but the ideas now work across almost every cloud platform. Today, businesses use these seven strategies to modernize systems, reduce costs, and support steady growth in the future.
For example, a small team might use these steps:
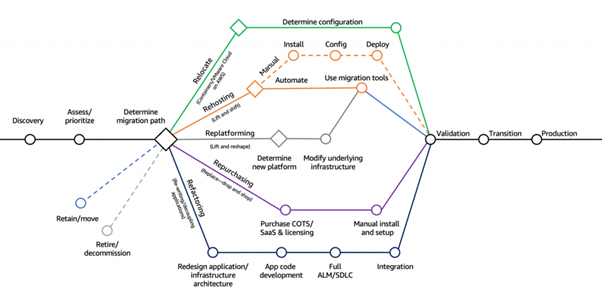
Below is a clear view of the seven strategies used by many companies during cloud moves. These AWS migration strategies shaped the modern the 7R models of migration or 7R migration strategies that guides teams through each important decision. The table helps you understand how each strategy works and when it fits your needs.
Strategy | Definition | When to Use | Difficulty |
Rehost | Move systems with no changes | Need fast and simple moves | Low |
Replatform | Make small improvements during migration | Improve performance with minor updates | Medium |
Repurchase | Replace tools with new SaaS products | Need quick upgrades with less maintenance | Medium |
Refactor | Rebuild apps for cloud models | Need long-term scale and modern design | High |
Retire | Remove unused tools or systems | Reduce clutter and lower cost | Very Low |
Retain | Keep some apps on-prem for now | Compliance or complex dependencies | Low |
Relocate | Move entire environments to cloud | Need fast infrastructure moves | Medium |
A table like this helps teams compare choices quickly and understand the 7R model at a glance.
Cloud migration strategies matter because they give teams a clear plan that removes guesswork from the entire move. These strategies break a complex process into simple steps that match real business needs. Many companies handle large systems, so clear steps help them avoid confusion and reduce unexpected issues. A defined strategy also keeps teams aligned, which supports better decisions during each phase of cloud migration.
Modern businesses follow these strategies because they want smoother work, safer changes, and stronger results. Cloud journeys often feel overwhelming, but a structured approach helps teams stay focused without rushing important choices.
Key reasons these strategies matter include:
A clear strategy makes the entire cloud migration process faster, smoother, and far less stressful because every step follows a proven path instead of guesswork.
The 7 Migration Strategies Explained (7R Model)
Rehosting is the quickest way to move from on-premise to the cloud. You take your existing applications and move them as-is, with no major code or architecture changes. It’s popular because it reduces complexity and gets companies into the cloud fast, especially when time and resources are limited.
A company moves its virtual machines directly to cloud VMs to stop maintaining costly physical infrastructure.
Relocating moves entire environments to the cloud without redesigning them. It is often used by companies that rely on virtualization platforms. This strategy offers a quick, low-risk path because teams shift workloads exactly as they run today. It reduces the need for deep planning and heavy technical changes.
A company moves all VMware workloads to a cloud-based cluster without making technical changes.
Replatforming keeps most of the application architecture intact but makes small improvements during the move. It’s a middle path; you get better performance, easier maintenance, and lower costs without committing to a full rebuild. This approach is trending because it blends speed with meaningful modernization.
A team migrates their self-managed database to a fully managed cloud database (like Amazon RDS) to reduce maintenance and improve reliability, without rewriting the entire app.
Refactoring rebuilds applications so they can use full cloud-native power. This includes microservices, event-driven designs, managed databases, and serverless computing. It is the most advanced strategy and delivers the best long-term results. But it often requires more time, money, and skilled developers.
A team rebuilds a legacy monolithic system into microservices to improve performance, scale, and deployment speed.
Repurchasing replaces existing software with cloud-based SaaS tools. Instead of fixing outdated systems, companies switch to modern platforms that come ready to use. This reduces maintenance work, cuts hardware costs, and gives teams faster access to new features. It’s a popular choice for businesses that want quick improvement without rebuilding everything.
A business leaves its outdated on-prem CRM and adopts Salesforce for better features and easier scaling.
Retaining means keeping some applications on-prem for now. Not every system needs an immediate cloud move. Some tools work better in their current environment until stronger reasons appear. This strategy lets teams focus on high-value migrations first while avoiding unnecessary pressure.
A financial application stays on local servers because compliance rules demand strict data control.
Retiring removes systems that are no longer useful or cost-effective. Many companies discover outdated tools during migration planning. Removing them reduces confusion, trims costs, and simplifies the entire cloud move. This strategy ensures teams only shift what truly matters.
A company shuts down an old reporting system to cut storage costs and reduce system complexity.
Choosing the right strategy requires a clear review of the entire environment. Each application has different needs, limits, and costs. A careful evaluation helps teams pick strategies that match long-term goals. This keeps cloud migration simpler, safer, and more aligned with business plans.
A structured approach helps teams avoid rushed decisions and reduces stress during migration. It also ensures each step supports lasting performance, better cost control, and clear growth.
How This Comparison Chart Works:
Use this chart to see how each strategy matches common goals.
Strategy | Cost | Speed | Risk | Modernization Level |
Rehost | Low | High | Medium | Low |
Replatform | Medium | Medium | Medium | Moderate |
Repurchase | Medium | Medium | Low | High |
Refactor | High | Low | High | Very High |
Retire | Very Low | High | Very Low | Low |
Retain | Low | High | Low | Low |
Relocate | Medium | High | Medium | Low |
Charts like this help teams pick strategies that fit their goals and constraints.
This chart gives teams a quick way to compare all seven migration strategies side by side. Each row shows how a strategy performs against common business goals.
These goals include cost, speed, risk, and modernization levels. By checking each column, teams can understand the strengths and limits of every strategy. Such knowledge makes it easier to choose the path that supports their plans.
This shows how much money the strategy usually requires. Lower-cost options need fewer changes and less work. Higher cost options often involve redesign, new tools, or bigger upgrades.
This tells how fast the migration can usually happen. High-speed strategies move quickly because they need fewer changes. Lower speed options take longer due to redesign or complex planning.
This shows how much uncertainty or disruption the strategy may create. Low-risk strategies use simple steps with fewer chances of failure. High-risk paths change many parts, which increases possible issues.
This tells how much the strategy upgrades or improves the system. Low modernization paths move systems as they are today. High modernization options use cloud-native features for better scale and performance.
Rehost has a low cost because it avoids deep changes. It moves fast but carries medium risk because old issues remain. It has low modernization since nothing major is improved.
Replatforming costs slightly more because it adds small upgrades. It offers a balanced speed and moderate modernization. Risk stays medium because some changes happen.
Repurchases use new SaaS products, so cost becomes medium. Speed stays medium because switching tools takes time. Risk is lower because vendors handle updates. Modernization becomes high due to new features.
Refactoring needs heavy redesign, so cost becomes high. Speed is low because rebuilding takes time. Risk is high due to large changes. Modernization becomes very high with cloud-native features.
Retire has a very low cost because it removes tools. Speed is high since deletion is simple. Risk stays very low because systems disappear. Modernization stays low because nothing new is added.
Retain has a low cost because nothing changes. Speed is high since teams keep tools as is. Risk is low because systems stay stable. Modernization stays low because updates are delayed.
Relocate has a medium cost because tools shift to cloud platforms. Speed stays high because no redesign is done. Risk becomes medium since environments move together. Modernization stays low because no major upgrades happen.
Companies often make predictable mistakes when planning cloud migration. Knowing these issues helps teams stay prepared.
Good planning reduces these risks and improves project outcomes.
A defined strategy builds stronger cloud migrations with fewer surprises. It helps teams avoid last-minute issues and budget problems.
A solid strategy supports teams across every migration stage.
CausalFunnel does not manage technical cloud migration tasks directly, but it becomes valuable after the move. Its AI tools study user behavior on cloud platforms and reveal patterns that improve conversions. This helps companies gain more value from their new cloud setup and justify migration costs.
How CausalFunnel adds value after migration:
How it connects to migration planning:
Different companies need different paths, so no single strategy works for everyone. The right choice depends on your goals, budgets, timelines, and future plans. These AWS migration strategies offer a clear framework to make smarter decisions.
Study your systems carefully and match the correct strategy to each application. This thoughtful approach ensures smoother cloud adoption and a stronger path to growth.
Start by auditing the app, its dependencies, and its performance needs. Then match those results to cost, timeline, and team skills.
Watch hidden dependencies, data loss, performance drops, and compliance gaps. Plan backups, staged testing, and rollback paths to reduce these risks.
Prioritize critical apps and low-risk workloads first for safer migrations. This phased approach reduces downtime and reveals hidden migration issues early.
Costs vary widely based on strategy, scale, and needed refactoring work. Estimate hardware savings, migration labor, SaaS fees, and ongoing cloud charges.
CausalFunnel analyzes user behavior post-migration to improve conversions and retention. Use its insights to justify migration ROI and guide product or marketing changes.
Start using our A/B test platform now and unlock the hidden potential of your website traffic. Your success begins with giving users the personalized experiences they want.
Start Your Free Trial
Empowering businesses to optimize their conversion funnels with AI-driven insights and automation. Turn traffic into sales with our advanced attribution platform.



