Free Funnel Audit
Convert more customers today!

SEO
10 mins read


SEO
10 mins read


SEO work often includes many tasks that repeat every single week. Teams check pages, review metadata, clean spreadsheets, and track rankings by hand. All these tasks take time and often cause small mistakes. Python helps reduce this slow manual work through simple automation. It can scan websites, clean data, and build reports in minutes. And, the good news is: You do not need a computer science degree to begin using Python today.
Many SEOs now use cloud tools that remove complex setup steps. Chat tools also help explain errors in simple human language. This makes learning Python easier than ever before for busy marketing teams.
When people ask how can Python be used for SEO, they usually want practical answers. They want clear use cases, not only technical theory. This guide focuses on real tasks that improve daily SEO work.
Python helps SEO teams work faster, cleaner, and with better accuracy. It supports many tasks that tools alone cannot customize well.
Here are the main reasons SEO professionals use Python today:
Python also supports programmatic SEO strategies used by large websites. These strategies create many pages using structured data and templates. Manual tools often fail when projects reach this scale.
Python scripts can also power reporting systems that update automatically. This removes the need for copying numbers between spreadsheets every week. Teams save hours while reducing human error.
Python becomes more valuable as websites grow larger and more complex. Small websites benefit too, but large projects feel the biggest impact.
Python works best when SEO tasks follow clear rules and are repeated often. These tasks consume time but do not require creative judgment.
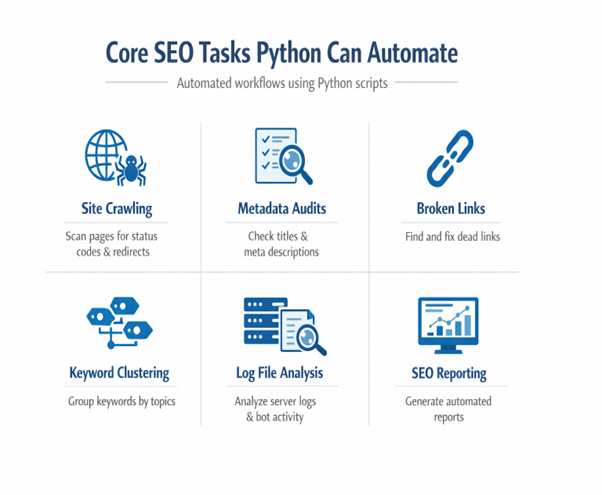
Below are common SEO jobs Python handles very well:
Python sends requests to pages and records server responses. It finds broken links, redirect chains, and slow pages quickly.
Python reads page titles and descriptions in bulk. It finds missing, duplicated, or overly long metadata automatically.
Python scans image tags for missing alt text attributes. This improves accessibility and image search visibility.
Python cleans keyword lists from research tools. It removes duplicates, groups similar phrases, and finds patterns.
Python studies server logs to understand real crawl behavior. This reveals which pages search engines visit most often.
Python pulls ranking data from tools and stores historical changes. It highlights sudden drops before traffic losses become serious.
Python builds dashboards that update from fresh data sources daily. Many teams treat these scripts as their own Python SEO tools.
Automation does not replace SEO thinking or strategy decisions. But it does remove busy work so that teams can focus on planning and optimization.
Python does not require deep programming knowledge to deliver SEO benefits. A few basic ideas support most useful SEO scripts.
These basics allow scripts to scan thousands of pages safely. They also prevent repeated mistakes caused by manual work.
Most SEO automation depends more on data handling than complex logic. Learning these tools unlocks most practical Python SEO use cases.
Python runs in various environments, depending on the comfort level and project size. Beginners often prefer cloud tools because they avoid setup problems.
Google Colab runs Python inside a browser window. It handles heavy data work without using your local computer memory.
Replit offers a simple coding space with built-in help tools. It works well for learning scripts and testing small projects.
These platforms allow fast sharing with teammates and clients. They also reduce errors caused by local installation problems.
Visual Studio Code with Python runs scripts directly on your computer. It provides full control over files and automation schedules.
Local setups work best for advanced projects and large data pipelines. They require more setup but offer greater long-term flexibility.
Most beginners should start with cloud tools first. Local setups become useful after you are more comfortable with simple scripts.
Python becomes powerful when applied to real SEO problems. These examples show how teams use scripts in daily operations.
Large websites contain thousands of pages and internal links. Manual checks miss problems hidden deep inside site structures. Python scans every page and records important technical signals, such as:
This audit runs in minutes instead of several working hours. Teams receive structured reports instead of messy spreadsheets.
Python reads page titles and descriptions from full site crawls. It flags pages with missing, duplicated, or weak metadata text.
This helps content teams fix problems faster and more consistently. It also improves search result appearance and click rates.
Python compares page text using similarity calculations. It highlights pages that repeat the same information often.
This prevents search engines from lowering site quality scores. It also protects websites from content cannibalization issues.
Keyword tools export large files that often contain noise. Python cleans this data and groups keywords by topic.
It also finds hidden trends across thousands of phrases. These insights guide content planning more accurately.
Some teams create their own lightweight SEO auditing scripts. This custom script checks important factors in one scan.
A basic Python SEO analyzer may review:
These tools match company rules instead of generic standards, and customizing them gives teams greater control over quality checks.
New learners should practice with small projects first. The following scripts teach real skills while solving actual SEO problems:
This script scans URLs and confirms secure protocol usage. It helps prevent browser warnings and trust issues.
This script finds images missing descriptive alt attributes. It improves accessibility and image search performance.
Python collects titles and descriptions into one spreadsheet. Writers then review content quality in bulk.
The script visits internal links and reports failed pages. This protects crawl budgets and user experience.
Python groups keywords by topic and intent. This supports better content planning decisions.
These projects teach data handling and logic naturally. They also provide immediate business value after completion.
Most major SEO platforms offer API access today. APIs allow direct data downloads without using web dashboards.
Python connects with many platforms, including:
This creates automated data pipelines for reporting and monitoring. Teams often combine multiple sources into one dashboard. Python cleans and merges this information into structured tables.
Many companies treat these workflows as internal Python SEO tools. They reduce dependency on expensive third-party software interfaces.
API-based automation supports:
Automation also prevents human mistakes during manual exports.
Python helps collect SEO data from APIs. Platforms like CausalFunnel help teams analyze SEO performance, user behavior, and conversions in one place, enabling them to understand what actually drives growth.
Python offers strong advantages, but does not fit every situation.
Here are common limitations:
Some tasks remain easier with standard SEO software tools. Python works best as a supporting system, not a replacement for other programming languages.
Python benefits certain SEO roles more than others. It is mostly helpful for:
Writers and small business owners may not need Python immediately. They can still benefit later when projects scale.

After learning basic scripts, many teams expand into advanced workflows. These systems run quietly in the background and support daily SEO decisions.
Python can check site health every morning before work begins. It scans important pages and reports serious problems early.
Common checks include:
This early warning system protects traffic from silent technical failures.
Python reviews content quality across thousands of pages automatically. It measures word count, duplication levels, and structure consistency.
Teams detect low-value pages before search engines penalize entire sections. This protects long-term domain authority and rankings.
Python helps manage structured data for programmatic SEO projects. It organizes location data, product attributes, and category rules.
Scripts validate page templates before public release. This prevents broken layouts and missing metadata.
Python analyzes historical traffic trends across long periods. It predicts future growth using simple mathematical models.
This helps teams plan budgets and resource allocation carefully. Clients also receive realistic expectations during reporting meetings.
Python tracks competitor ranking changes daily. It highlights sudden improvements or drops across shared keywords.
This allows quick responses to new strategies or content launches.
Strong habits prevent small errors from becoming serious technical issues.
Follow these guidelines for safer automation:
Automation should support human judgment, not replace it. Final SEO decisions must still involve careful review.
Learning Python for SEO does not have to feel overwhelming or technical. The most effective approach is to move in short, focused stages that match real SEO tasks. Instead of trying to master everything at once, SEO professionals can start with simple concepts and gradually build practical skills that improve daily work. This step-by-step method helps reduce frustration, builds confidence early, and allows you to see real results from automation in a short time.
A simple learning path includes:
Each stage builds confidence gradually. There is no need to rush advanced topics early. Consistent practice brings faster progress than long study sessions.
If you want to turn your SEO data into real business growth, explore the services of Causal Funnel. We assist clients in tracking how SEO traffic turns into real user actions and measurable business outcomes.
Python helps SEO teams save time and reduce mistakes. It turns large data problems into simple automated processes. Even basic scripts improve audits, reporting, and technical checks. Advanced systems support long-term growth and stability.
Learning Python does not require perfection or advanced programming skills. Small steps already deliver meaningful SEO benefits.
Start with simple tasks that solve real problems. Progress will follow naturally with practice.
You can use Python to automate tasks like site audits and broken link checks, clean messy keyword and traffic data in minutes, and build simple reports that update automatically.
No, Python does not replace professional SEO tools, but it complements them very well. It can pull data from their APIs, merge multiple datasets, apply custom rules, and generate reports that standard dashboards cannot easily create. This gives teams more flexibility and control over their SEO workflows.
Yes, Python helps you spot ranking gaps and weak pages using data, test changes like titles or internal links at scale, and even predict traffic trends for better planning.
Most SEO professionals can start building useful scripts within two to four weeks of consistent learning and practice. Mastering advanced automation and data analysis takes longer, but basic skills deliver value quickly and improve naturally with real-world projects.
Yes, Python can automatically collect data from Google Search Console, Google Analytics, and SEO tools, then organize it into clean tables and visual reports. These dashboards update on a schedule, reduce manual spreadsheet work, and provide more accurate insights into traffic, rankings, and conversions.
Start using our A/B test platform now and unlock the hidden potential of your website traffic. Your success begins with giving users the personalized experiences they want.
Start Your Free Trial
Empowering businesses to optimize their conversion funnels with AI-driven insights and automation. Turn traffic into sales with our advanced attribution platform.



