Free Funnel Audit
Convert more customers today!
SEO
10 mins read


SEO
10 mins read


You’re doing everything right. So why aren’t you seeing the results?
If you have ever wondered why some pages get traffic but no sales, or why great content never ranks, maybe your SEO funnel is not set up properly.
An SEO funnel explains how search visibility turns into real business outcomes. It shows how users move from discovering your site to taking meaningful actions. Without a clear funnel, SEO often drives traffic without driving results.
This guide explains the SEO funnel in a simple and practical way. You will learn how search engines process pages and how users make decisions. You will also learn how to connect these ideas into one working system.
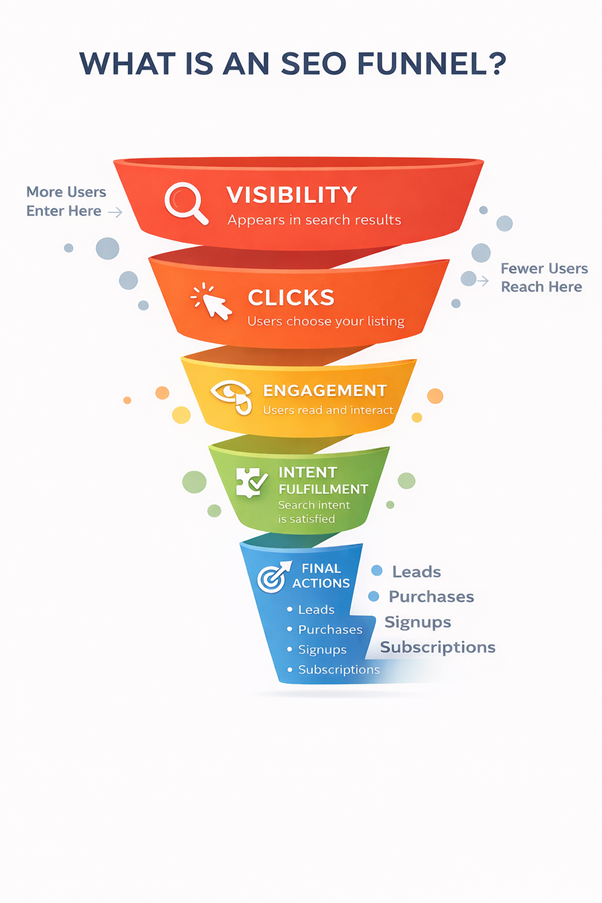
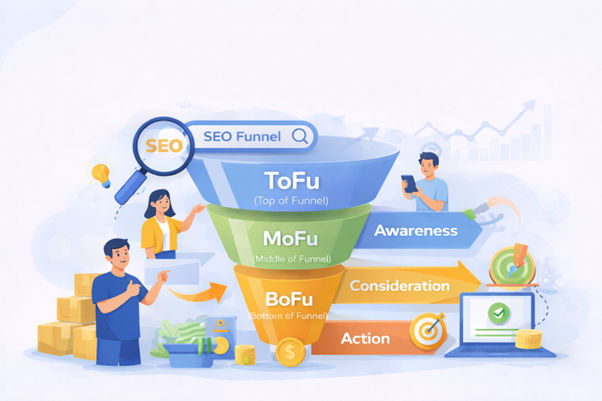
One of the most asked questions is what is a funnel in SEO? A funnel in SEO is a framework that explains how SEO produces results. It shows how many users enter at the top and fewer reach the bottom. Each stage depends on the previous stage working correctly.
The funnel starts with visibility in search results. It then moves through clicks, engagement, and final actions. Those actions may include leads, purchases, signups, or subscriptions.
Imagine someone planning to buy a coffee machine for home. They first search “how to make coffee at home” and land on an educational guide that explains brewing methods. Later, they search “best coffee machines for beginners” and read a comparison page that helps them evaluate options.
Finally, they search “buy espresso machine under $500” and land on a product page with pricing, reviews, and a clear purchase option. Each search reflects a different intent, and each page serves a specific purpose. That is how an SEO funnel works, guiding users from learning to deciding through search.
An SEO funnel focuses on outcomes, not just rankings. Traffic alone does not mean success without conversions. The funnel helps teams find where progress breaks down.
There are two main models used to explain the SEO funnel:
Both models describe the same journey from different viewpoints. Ultimately, strong SEO uses both models together, not separately.
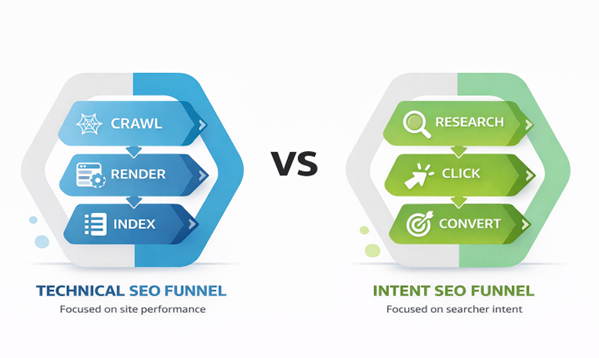
The SEO funnel can be viewed through two simple models. Each model helps solve a different SEO problem.
Technical SEO funnel stages:
This model is useful when pages are not appearing in search. For example, an ecommerce site may publish new product pages. If Google never crawls those pages, rankings will never happen.
Intent-based SEO funnel stages:
This model helps plan content and calls to action. For example, a SaaS company may attract many visitors through helpful guides and educational content. A smaller group later signs up for a demo or free trial. That is not always a bad sign. It can reflect a thoughtful buying process, higher acquisition costs, or the fact that customers need more time and information before making a decision.
You can use the technical funnel to diagnose visibility problems. On the other hand, the intent funnel guides you toward conversion.
Using them together, explain why SEO traffic does or does not convert.
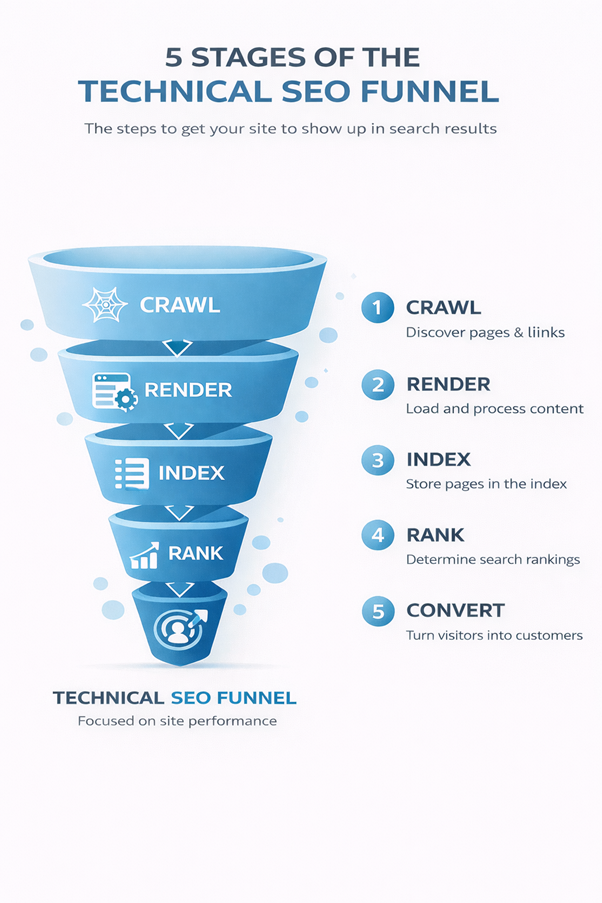
The technical SEO funnel explains how search engines process your website. It shows how a page moves from discovery to potential revenue. If a page fails early, it cannot succeed later.
For example, a blog post may be well written and useful. If search engines cannot crawl or index it, rankings never happen. Technical health always comes before content performance.
This funnel helps answer one critical question. Can search engines find, understand, and trust your pages?
Crawling is how search engines discover URLs on your website. Bots follow links and sitemaps to find new or updated pages. If a page is not crawled, it cannot be indexed or ranked and does not exist to Google. That sounds harsh, but it is true.
Most pages are discovered in three main ways:
For example, an online store launches fifty new product pages. If those pages are not linked internally, bots may never find them. As a result, the products never appear in search results.
Crawl budget refers to how many pages bots can visit regularly. Large websites often waste crawl budgets on low-value pages. This limits how often important pages are visited.
A few things quietly block crawling:
Crawl health checklist:
Rendering is when search engines load and view page content. This matters more than people think, especially with modern JavaScript sites. JavaScript-heavy sites often cause rendering issues.
Search engines must render content to understand it. If key content only appears after user interaction, search engines may miss it. Links hidden behind tabs or buttons can disappear from the crawl path.
For example, a SaaS homepage may load features using JavaScript. If features load after a click, bots may miss them. This reduces relevance and ranking potential.
Common rendering warning signs include:
To reduce risk, key content should load immediately. Important links should appear without user interaction.
Practical guidance helps here. Make sure your main content and links are visible in the initial HTML whenever possible. Search engines are better than before, but they are not browsers with patience.
Indexing is when search engines store your page data. Only indexed pages can appear in search results. Many pages fail here due to quality or clarity issues.
Search engines avoid indexing pages with weak value. Thin content and duplicates often get ignored. Conflicting signals also reduce indexing confidence.
For example, a blog publishes ten similar articles. Each article targets the same keyword with minor changes. Search engines may index only one and ignore the rest.
Indexing works best when pages have one clear purpose. Search engines prefer clarity over volume.
Index readiness checks:
If a page does not deserve to rank, it will not index long term.
Ranking happens when search engines choose the best answer for a query. This is not about tricks. It is about alignment.
They compare many pages for the same search query. Only the most relevant pages reach top positions.
Here, relevance matters more than keyword repetition. Pages should match the exact intent behind the query and one page should focus on one primary topic.
For example, a page targeting “SEO funnel” should explain the stages. It should not try to sell tools aggressively. This is because mixed intent weakens ranking signals.
Other ranking factors also play supporting roles:
Actions that improve rankings include:
Conversion starts earlier than most teams think. The first conversion is the click from search results. Strong titles and descriptions increase click-through rates. If titles and descriptions miss intent, traffic never arrives.
After the click, conversion depends on intent alignment. Different websites define conversion in different ways.
For ecommerce:
For SaaS or B2B:
For publishers:
Micro-conversions matter too:
The rule is simple. Match the CTA to intent. A TOFU blog should not push pricing pages. Instead, it should guide readers to deeper resources. BOFU pages should remove friction and show clear value.
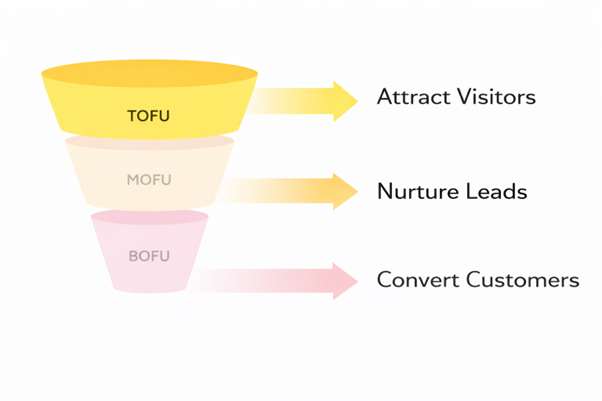
Now that we’ve mentioned the three most important terms in a funnel (TOFU, MOFU, BOFU) let’s see and understand what they really are.
The SEO marketing funnel focuses on user intent. People search differently at different decision stages. Content must match those changing needs.
Your job is to match intent with content and CTAs. When this clicks, SEO stops feeling random. This SEO funnel model helps guide users naturally.
TOFU searches come from early-stage users. These users want knowledge, not products or sales. Trust in the users begins at this stage. Research has shown that almost 68% leads come from search engines alone.
TOFU searches often include phrases like:
The best TOFU content educates clearly. It should avoid aggressive sales language.
Effective TOFU content includes:
Appropriate TOFU CTAs include:
Example TOFU searches and pages:
MOFU users understand the problem clearly. 64% online users compare options and approaches. They know the problem and want to choose a path. Therefore, they look for guidance.
MOFU searches often include:
MOFU content should explain differences clearly. It should help users choose confidently.
Strong MOFU content types include:
MOFU CTAs should feel supportive:
Example MOFU searches and pages:
BOFU users are ready to act. They want proof, clarity, and confidence. Any BOFU pages must remove doubt quickly. With the right content and proper SEO, 89% of the users go for a business that feels trustworthy.
BOFU searches often include:
BOFU pages must focus on conversion, and should answer final objections clearly.
High-performing BOFU pages include:
BOFU optimization checklist:

This is where platforms like CausalFunnel come into the scene. Their services help teams track full-funnel behavior, optimize conversion paths, personalize user journeys, and measure attribution across channels, which is exactly what BOFU optimization demands.

Building an SEO funnel requires clear planning. It does not happen by accident. A strong funnel starts with your business goal and works backward from conversion pages to supporting content. Each stage should guide users naturally to the next step.
Start by choosing the one action that matters most. This keeps your funnel focused and measurable.
Examples include a demo request, a lead form fill, a purchase, or a subscription. When your goal is clear, you can design every page to support it.
BOFU pages are your “money pages.” These are the pages that convert high-intent visitors.
Examples include pricing pages, service pages, product pages, booking pages, and demo pages. List them first because everything in your funnel should eventually lead toward them.
MOFU content helps users evaluate options and move closer to a decision. These visitors are interested, but not ready to commit.
Create pages like comparisons, “best options” lists, case studies, and solution guides. Then link them directly to the relevant BOFU page with a clear next step.
TOFU content brings in new traffic from broad, early-stage searches. These users want answers, not sales.
Create educational posts like definitions, beginner guides, how-to articles, and simple checklists. The job of TOFU content is to build trust and guide users into MOFU pages, not push them to buy instantly.
Internal linking is the “path” of your funnel. Without it, users and search engines may never reach the pages that matter.
Link TOFU → MOFU using contextual anchors, and MOFU → BOFU using intent-based CTAs. Add “next step” links that feel natural, not forced.
The biggest funnel mistake is using the same CTA everywhere. TOFU visitors need low-pressure options, while BOFU visitors need direct actions.
This improves conversions without hurting rankings.
Track performance by stage so you know what is breaking. Fix early issues before optimizing late-stage conversions.
If TOFU has impressions but no clicks, improve titles and match intent. If MOFU gets traffic but no BOFU clicks, improve internal pathways. If BOFU gets visits but no leads, improve proof, clarity, and friction removal.
Tracking the right metrics reveals funnel problems early. Each stage needs different measurements.
Technical funnel metrics include:
Intent funnel metrics include:
Always fix early-stage issues first. Late-stage optimization fails without a strong base.

Many SEO strategies fail due to poor funnel alignment. These mistakes appear across industries and often explain why traffic grows but results do not.
Early-stage visitors are not ready to buy. Pushing pricing pages or sales calls too early creates friction and weakens trust. Use low-pressure next steps like related guides, checklists, or newsletters instead.
For example, a blog post titled “What Is an SEO Funnel?” ends with “Book a Sales Call” as the main CTA. Most readers are still learning and leave without taking action.
Replace the CTA with “Read our SEO funnel stages guide” or “Download a free checklist” to keep users engaged and moving forward.
Great content fails when pages are isolated. TOFU pages should lead naturally to MOFU, and MOFU pages should guide users toward BOFU. Clear internal links help both users and search engines follow the funnel.
High-intent pages struggle when users are not prepared to decide. Without comparison guides, case studies, or solution explainers, BOFU pages feel abrupt. MOFU content builds confidence before the final step.
For example, a service page for SEO Consulting ranks for “hire an SEO agency”, but visitors are unsure how this agency compares to others. Instead, create MOFU pages like “SEO agency vs in-house team” or “How to choose the right SEO partner”, and link them to the service page.
Multiple pages targeting the same keyword confuse search engines. This splits ranking signals and weakens performance. Each page should own one primary intent and one main topic.
No funnel works if search engines cannot access your pages. Crawl, render, and index problems must be fixed before content optimization. Technical health is always the foundation.
Avoiding these mistakes strengthens your entire SEO funnel. When each stage supports the next, rankings improve and revenue becomes more predictable.
The SEO funnel gives structure to what often feels unpredictable. It explains why some pages never rank, why others attract traffic but fail to convert, and where effort is being wasted.
By fixing technical issues first, aligning content with TOFU, MOFU, and BOFU intent, and guiding users with the right calls to action, SEO stops being guesswork and starts becoming a system.
The real value of the SEO funnel is clarity. It shows what to fix, what to create next, and how each page contributes to real outcomes. When both the technical and intent-based funnels work together, SEO becomes easier to manage, easier to scale, and far more reliable in driving long-term growth.
An SEO funnel is a framework that explains how search traffic turns into real business outcomes. It shows how pages move from visibility in search results to clicks, engagement, and conversions. Instead of focusing only on rankings, the SEO funnel helps identify where progress breaks down.
A marketing funnel focuses on user behavior across channels, while an SEO funnel focuses specifically on search-driven journeys. The SEO funnel combines technical processes like crawling and indexing with intent-based stages like TOFU, MOFU, and BOFU. Together, they explain how search engines and users interact with your content.
Yes. Technical SEO ensures your pages can be discovered, indexed, and ranked. Intent-based SEO ensures users see the right content and CTAs at the right stage. Ignoring either side creates gaps that limit growth.
Results depend on competition, technical health, and content quality. Technical fixes can show impact quickly, while content-driven funnel improvements usually take weeks or months. The benefit is that results compound over time.
Track different metrics at each stage. Early stages focus on impressions and engagement, while later stages focus on assisted conversions and revenue. Measuring by stage helps identify exactly where optimization is needed.
Start using our A/B test platform now and unlock the hidden potential of your website traffic. Your success begins with giving users the personalized experiences they want.
Start Your Free Trial
Empowering businesses to optimize their conversion funnels with AI-driven insights and automation. Turn traffic into sales with our advanced attribution platform.



